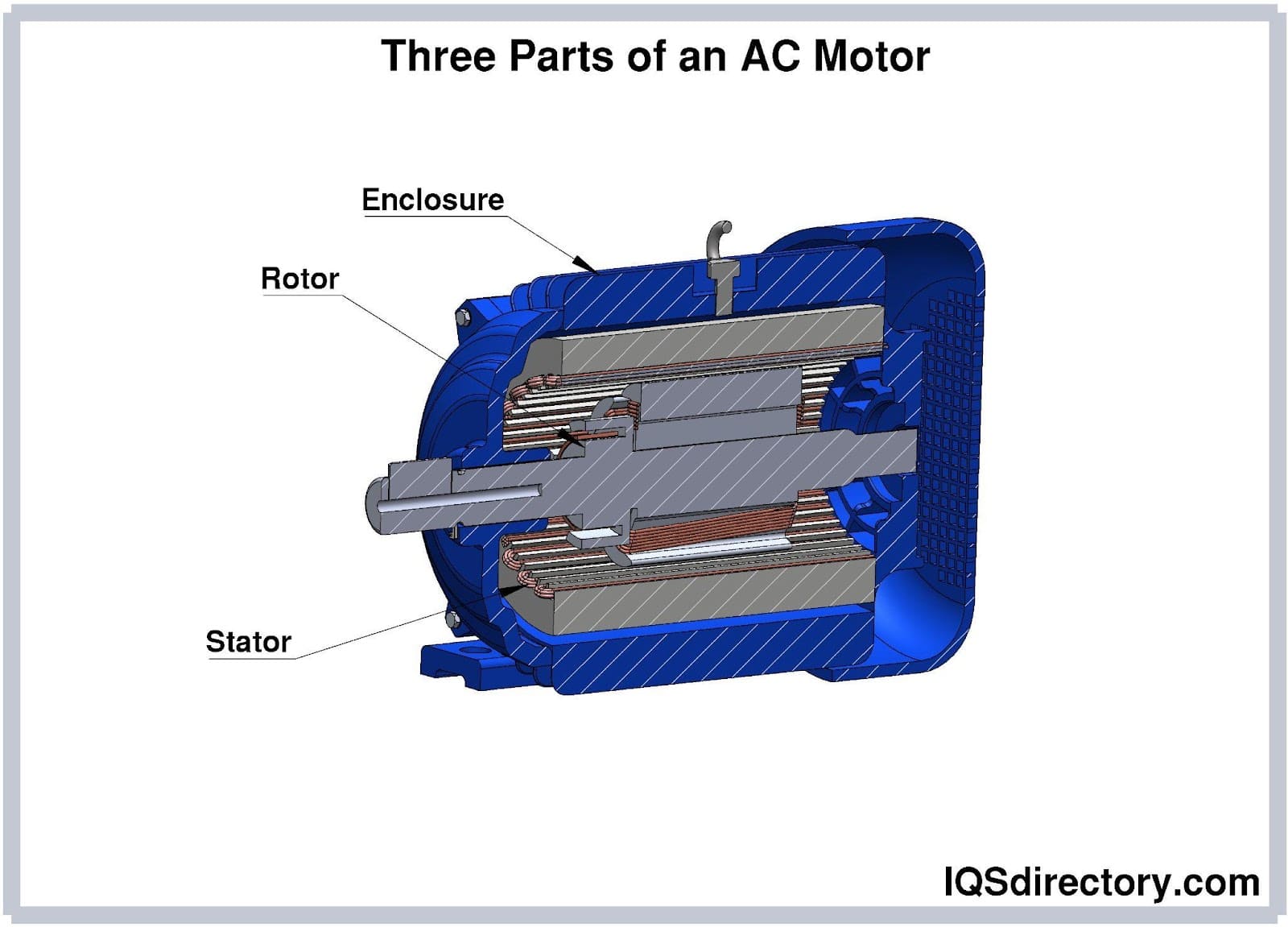
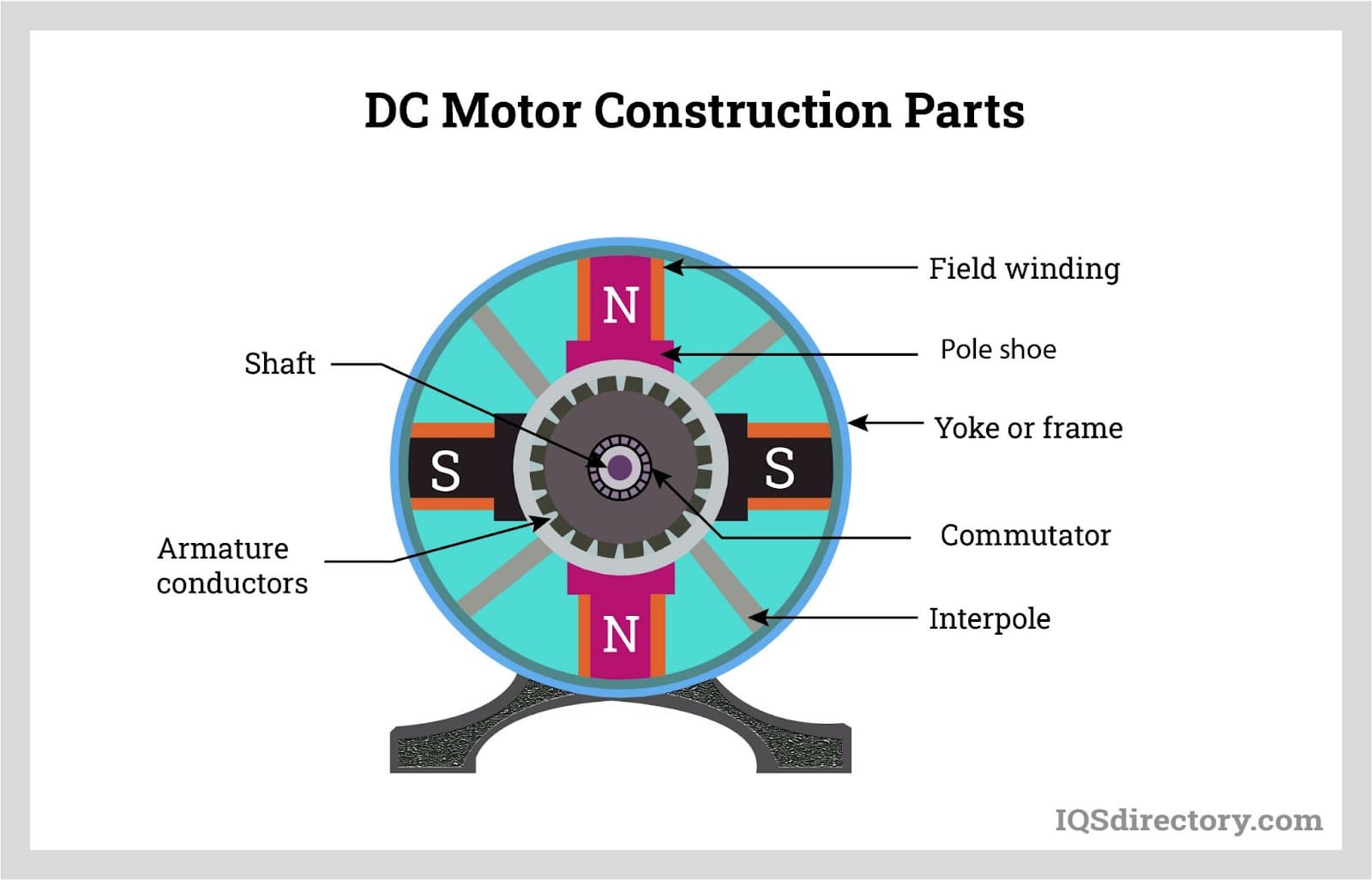
AutomationDirect.com specializes in providing a wide range of electric motors to meet our customers' diverse needs. Our commitment to excellence drives us to offer top-quality products that deliver superior performance and reliability. With our extensive selection of electric motors, ranging from AC motors to DC motors and everything in between, we empower industries to optimize their operations...
Since our inception in 1932, Carter Motor manufactures AC universal motors, small motors, DC universal motors, DC permanent magnet motors, DC shunt wound motors and gearmotors, and many others. All of our products are designed and assembled here in the USA. Our team is here to help you determine the best motor to fit your application and to ensure the process is efficient and stress-free. We are...
The products of Composite Motors, Inc. all undergo the same AS9100 certified design, manufacture and testing protocol. These products include Brushless DC motors, motor drivers, Lithium Ion batteries and Battery Management Systems, gear motors and linear actuators. All products are made in the USA from raw materials. Visit our website to learn more and to view our newest products.
We manufacture motors, motion control and rotating products for OEMs. The electric motors obtainable through us include AC motors, AC/DC motors, brushless DC motors, stepper motors.
Glentek, Inc. is a trusted provider of high-performance electric motors, specializing in innovative motion control solutions for a wide range of industries. We design and manufacture precision servo motors and amplifiers, delivering powerful and efficient performance for demanding applications. Our engineering expertise allows us to develop both standard and custom solutions, ensuring that each...

A leading supplier of high-performance motors and components, Chiaphua Components North America serves customers throughout the Americas and offers electric motors through the CCL & CIM Motor Products division. We supply motor solutions such as brushless motors, permanent magnet DC motors, induction motors, shaded pole motors, universal motors, vacuum cleaner motor, & gear motors.

More Single Phase Motor Manufacturers
A single-phase motor is a rotary electrical machine designed to convert electric energy into mechanical energy, making it a fundamental component in countless household and industrial applications. Operating on a single-phase AC power supply, these motors utilize two types of wiring: hot and neutral. Their simple construction and reliable operation have made them the preferred choice for various low to moderate power requirements across industries.
What is a Single-Phase Motor?
In essence, a single-phase AC motor is an electric motor that runs on a single alternating voltage. The supply voltages in a single-phase system rise and fall together in unison, and the circuit is typically composed of two wires, both carrying the same current. These motors are generally available up to 3KW (kilowatt) capacity, making them optimal for small to medium-scale applications where three-phase power is not accessible or necessary.
Unlike three-phase motors, single-phase motors do not inherently produce a rotating magnetic field. Instead, they generate only an alternating magnetic field, which is not capable of self-starting. To overcome this limitation, single-phase motors often rely on a capacitor or auxiliary winding to provide the necessary starting torque.
Key features of single-phase motors include:
- Simple construction and design
- Cost-effective compared to three-phase motors
- Suitable for light to moderate loads
- Widely available and easily maintained

How Does a Single-Phase Motor Work?
The operation of a single-phase induction motor is based on the principles of electromagnetic induction. When a single-phase AC supply is applied to the stator winding (also called the main winding), an alternating magnetic field—referred to as the main flux—is produced. This magnetic flux passes through the rotor, which is typically a squirrel cage type, and induces a current in the rotor circuit, as described by Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction.
The induced current in the rotor produces its own magnetic field, called the rotor flux. The interaction between the stator's main flux and the rotor flux generates torque, causing the rotor to turn and deliver mechanical energy to the connected load. However, because the stator field is simply alternating (not rotating), a single-phase induction motor does not generate starting torque on its own.
To address this, various starting mechanisms are employed. Many single-phase motors use an auxiliary winding and a start capacitor to create a phase shift, producing a rotating field and enabling self-start capabilities. Once the motor reaches a certain speed—typically 75% to 80% of synchronous speed—the start circuit may be disconnected by a centrifugal switch.
For further reading: Learn how DC motors compare to single-phase AC motors.
Summary of single-phase motor operation:
- Single-phase AC is applied to the stator winding
- Alternating main flux is generated
- Induced current in the rotor creates rotor flux
- Torque is produced via interaction of stator and rotor fields
- Starting mechanisms (e.g., capacitors) enable self-starting
Types of Single-Phase Motors
Single-phase induction motors are categorized primarily by their starting methods and construction, influencing their performance characteristics and suitability for different applications. The most common types include:
- Split Phase Induction Motor
- Shaded Pole Induction Motor
- Permanent Capacitor Induction Motor
- Capacitor Start Induction Motor
- Capacitor Start Capacitor Run Induction Motor
Split Phase Induction Motor
The split phase induction motor features two windings on the stator: the main winding and the starting (auxiliary) winding. The starting winding is highly resistive and connected in series with a centrifugal switch, while the main winding is more inductive.
The key purpose of the auxiliary winding is to create a phase difference between the currents in the two windings, resulting in a rotating magnetic field at start-up. Once the motor reaches a designated speed, the centrifugal switch disconnects the starting winding, allowing the motor to run on the main winding alone.
Typical applications: Fans, blowers, washing machines, small pumps, and other household appliances.

Shaded Pole Induction Motor
The shaded pole induction motor is one of the simplest and most cost-effective single-phase motors. It has salient poles in the stator, with a portion of each pole surrounded by a copper ring known as a shading coil. This coil delays the phase of the magnetic field, producing a weak rotating field sufficient to start the rotor.
While shaded pole motors offer low starting torque and efficiency, their simplicity and durability make them ideal for applications where minimal torque is sufficient.
Typical applications: Desk fans, exhaust fans, small appliances, and electric clocks.
Permanent Capacitor Induction Motor
In a permanent capacitor induction motor, a low-value capacitor is permanently connected in series with the auxiliary winding. This design provides a constant phase shift, resulting in a more balanced and efficient operation throughout the motor’s speed range.
These motors deliver high power factor, improved efficiency, and quiet operation compared to split phase motors. They are particularly suitable for continuous running applications that require moderate starting torque.
Key benefits:
- Higher efficiency and power factor
- Quiet and reliable operation
- Lower maintenance requirements

Capacitor Start Induction Motor
The capacitor start induction motor is an enhanced version of the split phase motor, addressing the latter’s low starting torque. Here, a high-capacity, dry-type capacitor is connected in series with the auxiliary winding during startup, creating a larger phase difference and thus significantly increasing starting torque.
After the motor achieves approximately 75% to 80% of its synchronous speed, a centrifugal switch disconnects both the auxiliary winding and the capacitor, allowing the motor to run efficiently on the main winding.
Key benefits:
- High starting torque suitable for heavy loads
- Reliable performance in demanding applications
- Efficient operation after startup

Capacitor Start Capacitor Run Induction Motor
This motor combines the advantages of both capacitor start and permanent capacitor designs by using two capacitors: a large-value start capacitor for high starting torque and a lower-value run capacitor for efficient continuous operation. The start capacitor is disconnected after startup by a centrifugal switch, while the run capacitor remains in the circuit.
Typical applications: Heavy-duty equipment, industrial machinery, and HVAC systems that require dependable performance under variable loads.
Advantages of Single-Phase Motors
Single-phase motors offer a variety of benefits that make them well-suited for domestic, commercial, and light industrial use. Understanding these advantages can help you determine whether a single-phase motor is right for your application.
- Affordability: Generally less expensive to purchase and install than three-phase motors, especially for lower power requirements.
- Availability: Compatible with standard household and commercial electrical systems, making them readily accessible worldwide.
- Compact size: Their simple design allows for smaller, lighter motors that can fit in tight spaces.
- Ease of maintenance: Fewer components and straightforward design facilitate easy servicing and repairs.
- Versatility: Suitable for a wide range of applications, from home appliances to office equipment and light industrial machinery.
Applications and Uses of Single-Phase Motors
Where are single-phase motors commonly used? These motors are found in a broad spectrum of residential, commercial, and industrial equipment due to their adaptability and efficiency. Here are some of the most common use cases:
- Home appliances: Refrigerators, freezers, washing machines, dishwashers, air conditioners, and vacuum cleaners all commonly utilize single-phase motors for reliable operation.
- HVAC systems: Fans, blowers, exhaust fans, and air handling units depend on single-phase motors for energy-efficient airflow control.
- Office equipment: Photocopiers, printers, and shredders harness the precision and cost-effectiveness of single-phase motors.
- Industrial applications: Small pumps, compressors, lathes, drills, and light-duty conveyors use single-phase motors for their affordability and ease of integration with standard power supplies.
- Other devices: Clocks, vending machines, and medical devices often incorporate single-phase motors due to their quiet operation and compact size.
Key Considerations When Selecting a Single-Phase Motor
Choosing the best single-phase motor for your needs involves understanding several critical factors to match your application requirements and operational environment. Here’s a checklist to guide your decision-making process:
- Power rating: Determine the necessary horsepower or kilowatt rating based on the load and duty cycle.
- Starting torque: Consider whether your application requires high starting torque (e.g., air compressors, pumps) or moderate torque (e.g., fans, blowers).
- Motor type: Select the appropriate motor type (split phase, shaded pole, permanent capacitor, etc.) for your specific use case.
- Voltage and frequency: Ensure compatibility with your local power supply (typically 110V or 220V, 50Hz or 60Hz).
- Size and mounting configuration: Match the motor’s physical dimensions and mounting style to your equipment.
- Efficiency and power factor: Higher efficiency motors reduce energy costs and environmental impact.
- Noise and vibration levels: Choose motors with noise and vibration characteristics appropriate for your environment (e.g., residential or office settings).
- Reliability and maintenance: Research manufacturer reputation and consider ease of maintenance for long-term operation.
How to Choose the Right Single-Phase Motor Manufacturer
Selecting a reliable single-phase motor manufacturer is essential for ensuring optimal product quality, consistent supply, and dedicated after-sales support. Here are some actionable steps to help you find the best supplier for your project:
- Research industry experience: Look for manufacturers with a proven track record in designing and producing single-phase motors for your desired application or industry.
- Evaluate certifications: Check for compliance with international standards such as ISO, CE, and UL to ensure safety and reliability.
- Review technical support and customization options: Reliable manufacturers offer engineering support, application advice, and the ability to custom-design motors for unique requirements.
- Compare warranties and after-sales services: Strong warranty coverage and responsive customer service are indicators of a reputable manufacturer.
- Check supply chain and lead times: Ensure the manufacturer can meet your delivery schedule and volume demands.
Ready to start sourcing? Our directory of single-phase motor manufacturers provides company profiles, areas of expertise, and direct contact forms for easy communication. Use our patented website previewer to compare suppliers and submit your requests for quote (RFQ) to multiple manufacturers using a single, convenient form.
Frequently Asked Questions About Single-Phase Motors
What are the main differences between single-phase and three-phase motors?
The primary distinction lies in the power supply: single-phase motors use a single alternating current, while three-phase motors utilize three currents phase-shifted by 120 degrees. Single-phase motors are typically used for low to moderate power applications, offering simpler installation and lower costs, whereas three-phase motors provide higher efficiency, greater starting torque, and are suited for heavy-duty industrial uses.
When should I use a single-phase motor instead of a three-phase motor?
Single-phase motors are ideal for applications where three-phase power is unavailable, unnecessary, or cost-prohibitive. Typical use cases include household appliances, small machinery, light-duty pumps, and fans.
How do I determine the correct size and type of single-phase motor for my application?
Assess your application's load requirements, startup torque needs, operating voltage, and environmental conditions. Consult product datasheets and seek guidance from motor manufacturers or technical specialists to ensure optimal selection.
Where can I find technical support and replacement parts for single-phase motors?
Many reputable single-phase motor manufacturers provide ongoing technical support, spare parts, and repair services. Using a directory with verified suppliers makes it easier to source original components and access expert assistance.
What maintenance is required for single-phase motors?
Routine maintenance includes periodic inspection, lubrication (if applicable), checking for overheating, ensuring clean air flow, and verifying proper electrical connections. Always follow the manufacturer's recommended maintenance schedule for optimal performance and longevity.
Summary: Why Choose a Single-Phase Motor?
Single-phase motors continue to be the go-to solution for a wide variety of low- to medium-power applications thanks to their affordability, simplicity, and adaptability. Whether you’re outfitting home appliances, office equipment, or light industrial machinery, these motors offer dependable performance with low installation and operational costs.
To make an informed purchase decision, always consider your application's unique requirements, compare technical specifications, and evaluate reputable manufacturers. For more information, contact leading single-phase motor suppliers using our directory and RFQ tools.
Still have questions? Contact our team of electric motor specialists for expert advice and personalized recommendations.





 Ball Bearings
Ball Bearings Ball Screws
Ball Screws Electric Motors
Electric Motors Friction Materials
Friction Materials Gears
Gears Quick Release Couplings
Quick Release Couplings Shaft Couplings
Shaft Couplings Speed Reducers
Speed Reducers Timing Belting
Timing Belting Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services